Trained Immunity and Beta 1,3/1,6 Glucan
Trained Immunity is not new in being real; here since creation, but is new in being the new research area gaining recognition and acceptance by scientists. While most explanations are very complex requiring a medical dictionary, recent extensive research can be reviewed at www.betaglucan.org under the alphabetical research listing category “Trained Immunity.” Two of the most recent studies are listed below:
*Trained Immunity – B-glucans: Mata-Martinez, Bergon-Gutierrez, Fresno CD, “Dectin-1 Signaling Update: New Perspectives for Trained Immunity,” Front Immunl;13:812148, https://doi.org/10.3389/fimmu.2022.812148 , PMID: 35237264, Feb 14, 2022. Quote: “Dectin-1 [as a B-glucan cell receptor] has recently gained a renewed attention due to its role in the induction of trained immunity. This process of long-term memory of innate immune cells can be triggered by B-glucans, and Dectin-1 [as a B-glucan cell receptor] is crucial for its initiation.”
*Trained Immunity – B 1,3/1,6d glucans: Vetvicka V, Sima P, Vannucci L, “Trained Immunity as an Adaptive Branch of Innate Immunity,” Int J of Mol Sciences, 22(19), PMID: 34639025, https://doi.org/10.3390/ijms221910684 , Oct 01 2021, “As more studies have confirmed the existence of trained immunity, …trained immunity effects induced by …products such as …B-glucans…are accompanied by a more effective cytokine response, which could lead to improved antiviral protection, even from the coronavirus disease, COVID-19. …B-Glucan-induced trained immunity has been suggested as an effective way to boost immune response against COVID-19 infection and even to abrogate [eliminate] symptoms. “
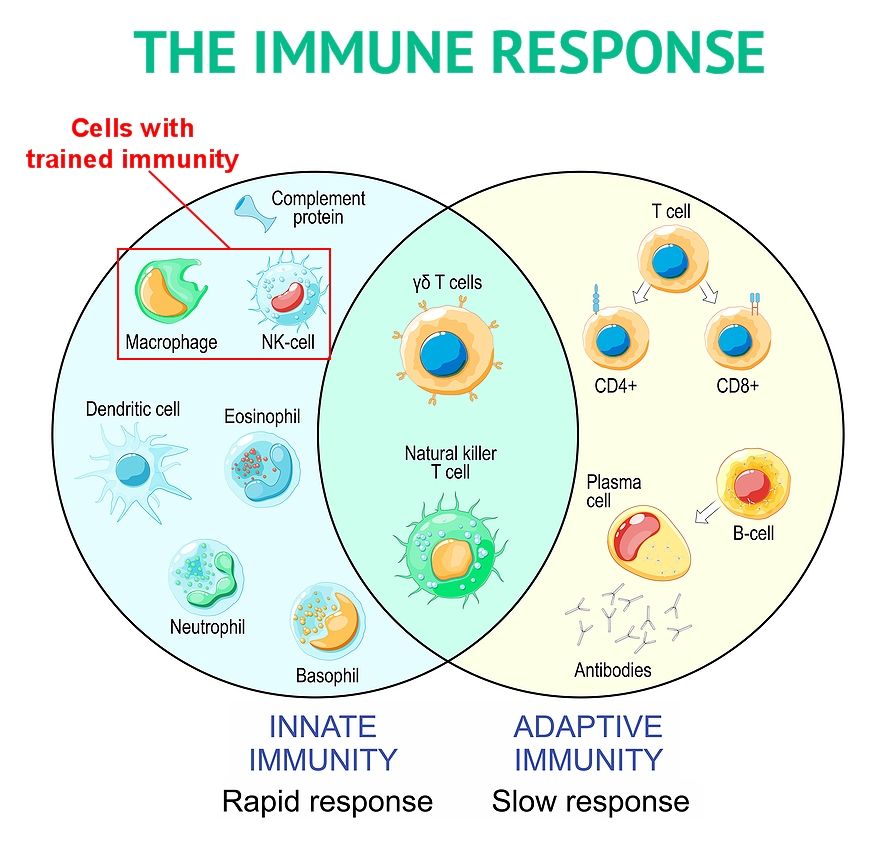
The science of immunology divides the immune responses in the body into two areas – innate/natural and adaptive. The adaptive is slower but is more thorough in classifying non-self as safe or pathogenic/dangerous to health. If deemed pathogenic after presentation by antigen presenting cells (apc’s) of microbe name tags to the immune lab cells (B cells), antibodies are produced that after usually 5-7 days provide an evaluation that if dangerous sounds the alarm for your personal immune cells to respond (see the attached chart) and hopefully kill and dispose of the invasion threats.
The second part of your immune response is the innate immune system that has always been thought to be a non-specific responding beat policeman that reacts immediately if a body intruder is suspected not to belong in the body. The innate immune cells, headlined by macrophages and NK or Natural Killer cells, have for most immunologists been deemed capable of a rapid first response, but without a memory of health threats previously encountered and no specialized weapons such as the specific antibodies that are designed to attack specific health threats.
Times change and now most immunologists recognize that certain immune cells, including macrophages and NK cells, can establish a form of memory of prior pathogen encounters and thus offer a faster and somewhat specific immune response. While not as powerful in memory, the immediate innate response versus the delayed response of the adaptive immune response can provide a better immediate immune reaction to pathogens, including many viruses, until the much slower adaptive response with antibodies for a unique pathogen arrives.
An additional benefit of trained immunity by innate immune cells is the attack against health invaders is not specific to a single pathogen as with the adaptive response, but universal in its defense of the bodies cells. In other words, the trained immunity by macrophages and NK cells enables an immediate non-specific attack on multiple viruses or microbes and not just a bullet for a single threat.
A major nutritional trigger to activate and create a trained immunity response is beta 1,3/1,6 glucan recognized as GRAS or safe and subject to thousands of research studies with most listed by health issue involved in the research at www.betaglucan.org, a non-commercial site. Trained immunity simply refers to the fact certain innate immune cells, once exposed to an invading health threat symbolized by a pathogen or various pathogens, does create a memory to enable an even more rapid activated innate immune response if confronted again by the same pathogen – a great potential aid to the overall immune response by the body – innate and adaptive – in our body war to stay healthy and alive.
Be aware and thankful we have both an innate and adaptive immune response that act together against health threats to recognize, respond, resolve and remove these dangers to our well-being.